In the previous post, we’ve created a workload domain with a cluster. In your VMware Cloud Foundation environment, you can stretch workload domain clusters in the management domain or in the VI workload domain across two availability zones. More on availability zones can be found in the documentation.
As always, before you begin, check the requirements for a stretched workload domain cluster in the documentation.
Note – Once a cluster is stretched, you cannot un-stretch it.
Stretching vSAN clusters in VCF does not differ much from the procedure used in the conventional vSAN stretched cluster. However, there is one exception. You have to add the hosts from the secondary site to the cluster using a script that is executed on the SDDC Manager.
At this point I assume you already have a workload domain up and running and you have a number of hosts pre-configured on the secondary site that are commissioned in the SDDC Manager.
Note – Ensure that you have a vSAN Enterprise license, which is required for stretching a cluster!
Stretch Workload Domain Cluster
- First, go to VMware KB 59280 and read the document. Download the script archive file from the attachments pane on the right.
- Upload and unpack the tar archive on the SDDC Manager by running: # tar xf <archive.tar>

- Open SSH session to the SDDC manager and login as the vcf user.
- Run the stretch_vsan.py script. For example, if you want to create a stretched cluster with 8 nodes, you need to add 4 hosts on the secondary site as follow:
# python stretch_vsan.py --stretch-vsan --domain WLD-1 --cluster Cluster-1 --hosts host-1b.vcf-1.dr.local host-2b.vcf-1.dr.local host-3b.vcf-1.dr.local host-4b.vcf-1.dr.local --license XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX - This command triggers the stretch workflow. Wait until this workflow completes. You can monitor the progress in the Tasks pane.
- Deploy the vSAN witness and configure the management IP settings for VMkernel (vmk0) adapter including DNS and hostname.
- Add the vSAN witness to the vCenter Server inventory and use the pre-assigned license key for the witness host. Configure the witnessPg (vmk1) adapter for vSAN traffic and enter the TCP/IP settings.
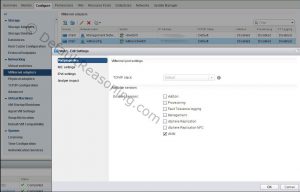
- Select the cluster that is going to be stretched. From the Configure tab go to Fault Domains & Stretched Cluster. Click the Configure Move the hosts added to the cluster in step 4 to the Secondary Site.
- Select the vSAN witness host from the inventory.
- Verify the disk layout and click Next.
- Review the settings and click Finish to configure the stretched cluster. Once the configuration is completed, you should see 2 failure domains.
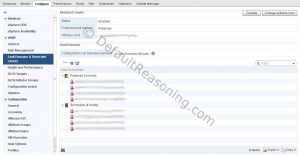
- With the cluster object still selected, edit the vSphere Availability Set the following settings:
- Host Failure Response: Restart VMs
- Response for Host Isolation: Power off and restart VMs.
- On the Admission Control page, enter appropriate number of host failures cluster tolerates. For stretched cluster reserve 50% of the resources. In this example, in an 8-host cluster, user value of 4 for 50% reservation.
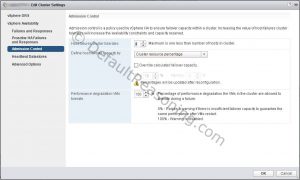
- On the Advanced Options page, add the following values:
- usedefaultisloationaddress=false
- isolationaddress0 = physical isolation address on primary site
- isolationaddress1 = physical isolation address on secondary site
- Click OK to save the settings.
The cluster in now stretched across 2 sites but there are some additional steps that needs to be done before the configuration is completely finished.
Post Deployment Tasks
- Create new vSAN storage policy – create a rule set that includes Primary (pFTT) and Secondary (sFTT) Level of Failures to Tolerate.
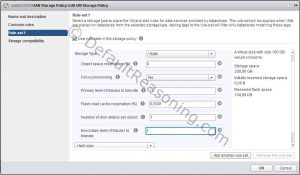
- Enable vSAN Performance Service – verify that the vSAN Performance Service is running and assign the new vSAN storage policy to the cluster.
- Create host groups – one group for the preferred site and one for the secondary site. Add the hosts to the groups accordingly.
- Create virtual machine groups for:
- NSX Controllers – create an anti-affinity rule to separate the NSX controllers.
- NSX Edges – (if any) create an anti-affinity rule to separate the NSX Edges.
- NSX DLR’s – (if any) create an anti-affinity rule to separate the DLR’s.
When the post deployment tasks are finished the stretch workload domain cluster configuration is completed.
Cheers!
Marek.Z
Be the first to comment